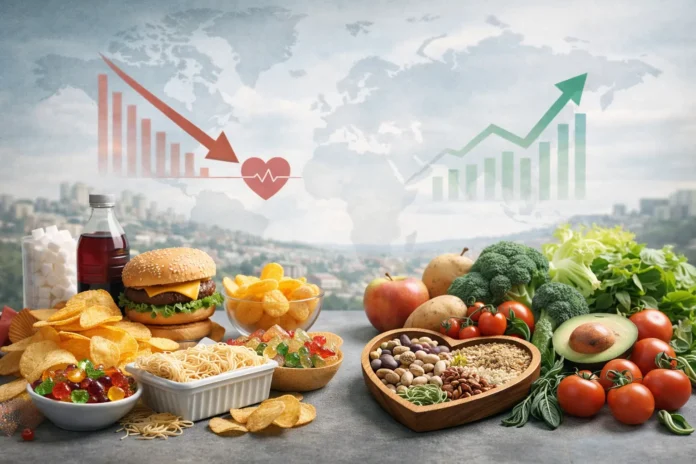
Ultra-processed foods have become a staple for billions of people worldwide.
Yet their long-term effects on health are far more serious than many realize.
These foods are quietly affecting global health by driving chronic disease and nutritional deficiencies.
What Are Ultra-Processed Foods?
Ultra-processed foods are industrial products primarily made from refined ingredients, additives, and preservatives.
Companies create these foods to be easy to use, long-lasting, and highly appealing in taste.
Common examples include packaged snacks, sugary cereals, instant noodles, soft drinks, and ready-to-eat meals.
Why Ultra-Processed Foods Are So Widely Consumed
They are cheap, accessible, and aggressively marketed.
Busy lifestyles and urban living have made convenience a priority over nutrition.
In many countries, ultra-processed foods now make up more than half of total calorie intake.
Long-Term Health Impacts
Increased Risk of Chronic Disease
Regularly eating these products can lead to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
High sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium levels disrupt metabolic health over time.Poor Gut and Digestive Health
Artificial additives and low-fiber content disrupt the balance of gut microbiota.
This imbalance weakens the immune system and raises inflammation.Nutrient Deficiencies
Ultra-processed foods are calorie-dense but nutrient-poor.
They often replace whole foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals.Mental Health Effects
Emerging research links high intake to depression and cognitive decline.
Blood sugar spikes and inflammation may contribute to these effects.
Ultra-Processed Foods vs. Whole Foods
| Aspect | Ultra-Processed Foods | Whole Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Density | Low | High |
| Fiber Content | Minimal | Naturally rich |
| Additives | High | None |
| Long-Term Health Impact | Negative | Protective |
This contrast highlights why dietary patterns matter more than individual calories.
Global Health Consequences
Rising consumption is straining healthcare systems worldwide.
Chronic illnesses linked to diet now account for the majority of preventable deaths globally.
Lower-income populations are disproportionately affected due to cost and access barriers.
Why This Is a Global Issue
Consumption of ultra-processed foods is rising most rapidly in developing economies.
As traditional diets disappear, diet-related diseases follow closely behind.
It makes nutrition a public health, economic, and social stability issue.
How to Reduce Reliance on Ultra-Processed Foods
- Prioritize minimally processed whole foods
- Read ingredient labels carefully
- Cook more meals at home
- Replace sugary drinks with water or unsweetened alternatives
- Focus on balanced, sustainable eating habits.
Even minor adjustments can lead to significant improvements in long-term health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are all processed foods unhealthy?
No. Minimally processed foods, such as frozen vegetables or yogurt, can be part of a healthy diet.
Why are ultra-processed foods linked to obesity?
These foods can drive overconsumption by disrupting the body’s natural sense of when it is full.
Would it be possible to include ultra-processed foods in a healthy diet?
Occasional consumption is unlikely to cause harm, but regular intake increases risk.
Do ultra-processed foods impact children differently?
Yes. Early exposure can influence lifelong eating habits and health outcomes.
Is avoiding ultra-processed foods realistic?
Complete avoidance is difficult, but reducing intake offers clear health benefits.
- The 15 Most Effective Natural Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- 10 Proven Ways to Burn Calories Without Exercise