Belgium enchants visitors with its historic cities, world-famous chocolate, and pivotal role in the European Union. Yet beneath this charm, the country faces pressing social, economic, and environmental challenges. Millions of Belgians are affected by political deadlocks, regional economic disparities, climate risks, and housing shortages, all of which are shaping the nation’s future.
This article examines the 10 major problems in Belgium, providing key facts and insights to explain their impact and significance.
Here Are The 10 Biggest Problems in Belgium
Political Fragmentation
Linguistic divisions and Belgium’s federal structure often lead to political deadlocks. The complexity and instability of coalition governments slow policymaking and impede reforms.Economic Inequality
Significant economic disparities exist between Flanders, Wallonia, and Brussels. While Flanders enjoys higher employment rates and stronger economic output, Wallonia faces persistent unemployment and lower productivity, impacting social mobility and national cohesion.Aging Population
Belgium, like many European nations, has an aging population. A growing number of retirees increases pressure on pensions, healthcare services, and the labor market, raising concerns about long-term economic sustainability.Youth Unemployment
Despite overall economic stability, youth unemployment remains a concern, especially in Wallonia. Young Belgians face challenges entering the labor market, which can lead to delayed independence, underemployment, and potential brain drain.Immigration and Integration
Belgium receives a substantial number of immigrants each year. While immigration supports the labor force, integration challenges remain, including access to education, social inclusion, and public perception, which affect social cohesion.Climate Change and Environmental Risks
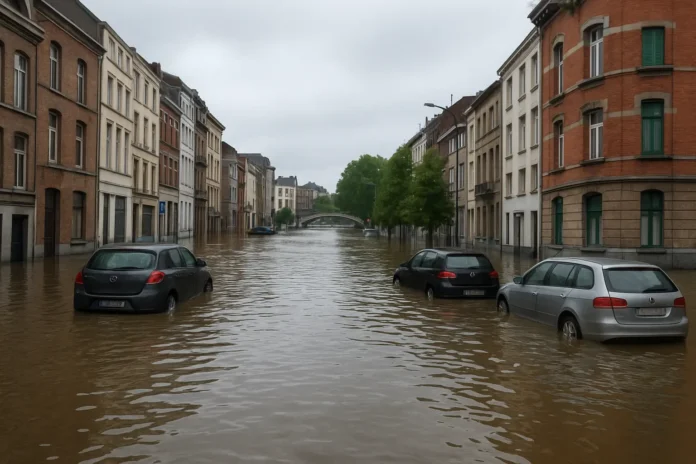
Belgium is vulnerable to flooding, heatwaves, and pollution, particularly in urban areas and low-lying regions. Extreme weather events have already caused property damage and economic disruption, highlighting the need for proactive environmental policies.Housing Shortages
Property prices and rents have risen sharply in major cities like Brussels and Antwerp, creating affordability issues. Limited social housing and slow urban planning fail to keep pace with increasing demand.Healthcare Strain
Belgium’s healthcare system offers high-quality services, but regional disparities, staffing shortages, and growing demand create pressure. Access can be uneven, particularly in rural areas or for low-income families.Transportation and Infrastructure Challenges
Traffic congestion, aging roads, and disparities in regional transport networks hinder mobility and economic efficiency. Public transport quality varies, and infrastructure investments often face bureaucratic delays.Public Debt and Fiscal Pressures
Belgium’s public debt reaches roughly 100% of GDP, posing a significant economic burden. It limits government spending flexibility, affects fiscal policy, and constrains public investment in infrastructure, healthcare, and education.
Authoritative Sources for Belgium’s Biggest Problems
| # | Problem | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Political Fragmentation | Highlights governance challenges, coalition complexity, and linguistic divisions influencing policymaking. |
| 2 | Economic Inequality / Regional Disparities | Provides data on regional disparities, income differences, and social sustainability issues. |
| 3 | Aging Population | Shows demographic trends, population aging, and dependency ratios. |
| 4 | Youth Unemployment | Provides statistics on youth unemployment, employment rates, and labor market challenges. |
| 5 | Immigration & Integration | Examines migrant integration and its impact on employment and social cohesion. |
| 6 | Climate Change & Environmental Risks | Provides data on climate vulnerability, flooding, and environmental challenges. |
| 7 | Housing Shortages / Affordability | Highlights rising property prices, increasing rental pressures, and difficulties in providing adequate social housing. |
| 8 | Healthcare Strain | Details healthcare capacity, regional disparities, and staff shortages. |
| 9 | Transportation & Infrastructure Challenges | Covers urban mobility, transport inefficiencies, and infrastructure planning issues. |
| 10 | Public Debt & Fiscal Pressures | Provides analysis of Belgium’s debt, fiscal deficits, and economic risks. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main economic challenge in Belgium?
Regional economic disparities and high public debt are the primary economic challenges, impacting growth and investment.
Why is political fragmentation a concern?
Frequent coalition negotiations and linguistic divisions slow policymaking and can delay reforms across key sectors.
How is Belgium affected by climate change?
Flooding, heatwaves, and pollution threaten infrastructure, property, and agriculture, requiring proactive mitigation measures.
What regions face the most housing challenges?
Brussels, Antwerp, and other major cities struggle with rising rents and a shortage of social housing, which impacts affordability.
How is youth unemployment being addressed?
Programs include vocational training, employment incentives, and regional economic development initiatives, though results vary.
Final Word
Belgium is a country of remarkable history, culture, and economic significance, but it faces a complex set of intertwined challenges. Political fragmentation, economic disparities, climate risks, and social pressures require coordinated policy responses and long-term planning.
- The 10 Biggest Problems in Greece
- The 10 Biggest Problems in Spain
- The 10 Biggest Problems in Denmark